单层铁硒(FeSe)薄膜生长在钛酸锶(SrTiO3)衬底上之后,可以获得约65 K的超导配对温度,相对于FeSe块材得到了极大的提高,引发了人们广泛的兴趣和关注。其中氧化物衬底与FeSe薄膜之间的界面被认为对超导增强起到了重要作用。通过改换衬底,探索不同界面对FeSe薄膜的超导电性的影响可以为进一步研究其中的超导机理提供关键的信息。此前人们仅在SrTiO3、BaTiO3、TiO2等几种钛氧化物衬底与单层FeSe形成的FeSe/TiOx界面中发现高温超导。我们尝试在一种非钛氧化物——铁酸镧(LaFeO3)衬底上生长单层FeSe薄膜,成功获取了高质量的样品。我们利用高分辨的扫描透射电镜(STEM)确定了它具有一种全新的FeSe/FeOx界面,并在这个体系中观察到了17 meV的超导能隙,以及相应的80 K的超导配对温度,这在目前所有的界面超导体系中是最高的。该体系也是第一个FeSe/TiOx界面以外的具有高温超导的界面体系。更为重要的是,我们在该体系中验证了界面电声子相互作用对超导的增强机制在FeSe与氧化物形成的界面超导当中是普适的。同时,通过将FeSe/FeOx与FeSe/TiOx界面对比,我们发现通过缩短界面间距可以提高界面电声子耦合强度从而增强超导,为将来设计高温超导界面提供了全新的思路。
论文见:Y. H. Song, Z. Chen, Q. H. Zhang, H. C. Xu, X. Lou, X. Y. Chen, X. F. Xu, X. T. Zhu, R. Tao, T. L. Yu, H. Ru, Y. H. Wang, T. Zhang, J. D. Guo*, L. Gu*, Y. W. Xie*, R. Peng*, D. L. Feng*, High temperature superconductivity at FeSe/LaFeO3interface, Nat. Commun. 12, 5926 (2021)
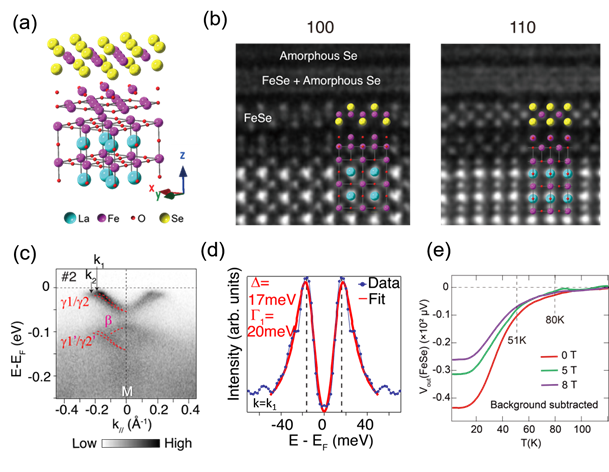
图:(a)单层FeSe/LaFeO3原子结构示意图(b)扫描透射电镜高角环形暗场像(c)角分辨光电子能谱得到的样品布里渊区M点能带(d) M点费米穿越处超导能隙(e)不同磁场下的互感抗磁信号
Discovering the high temperature superconductivity and interfacial enhancement mechanism of FeSe/LaFeO3interface
Monolayer iron selenide (FeSe) films grown on strontium titanate (SrTiO3) substrates can boost superconducting pairing temperature to about 65 K, igniting intensive research interests. The interface between oxide substrate and FeSe film is believed to play an important role in the superconductivity enhancement in FeSe/SrTiO3. Exploring the effect of different kinds of interfaces on the superconductivity of FeSe films by changing substrate can provide key information for studying their superconductivity mechanism. Previously, high temperature superconductivity was found merely in the FeSe/TiOx interfaces formed between monolayer FeSe and titanium oxide substrates such as SrTiO3, BaTiO3and TiO2. We tried to grow a monolayer FeSe film on a non-titanium oxide, lanthanum ferrite (LaFeO3), and successfully obtained high-quality samples. Using high-resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM), we identified that it has a novel FeSe/FeOx interface. In this interface, a superconducting gap of 17 meV and a corresponding superconducting pairing temperature of 80 K were observed. The FeSe/LaFeO3interface has the highest pairing temperature among all the superconducting interfaces at present, and it is also the first interface with high temperature superconductivity beyond FeSe/TiOx. More importantly, in the FeSe/LaFeO3interface, we verified that the enhancement mechanism of interfacial electron-phonon interaction on superconductivity is universal for the FeSe/oxide interfaces. At the same time, by comparing the FeSe/FeOx and FeSe/TiOx interfaces, we found that by decreasing the interfacial spacing, the interfacial electron-phonon coupling strength can be increased to enhance superconductivity, which provides a new perspective on the design of high temperature superconducting interfaces in the future.
Reference:Y. H. Song, Z. Chen, Q. H. Zhang, H. C. Xu, X. Lou, X. Y. Chen, X. F. Xu, X. T. Zhu, R. Tao, T. L. Yu, H. Ru, Y. H. Wang, T. Zhang, J. D. Guo*, L. Gu*, Y. W. Xie*, R. Peng*, D. L. Feng*, High temperature superconductivity at FeSe/LaFeO3interface, Nat. Commun. 12, 5926 (2021)

Figure(a) Illustration of the atomic structure of monolayer FeSe/LaFeO3
(b) High-angle annular dark field images by scanning transmission microscopy
(c) Band structure of the sample around the M point of Brillouin zone by ARPES
(d) Superconducting gap at the Fermi crossing around M point
(e) Diamagnetic signals measured by mutual inductance under different magnetic fields